Measurement is an essential part of our everyday lives, whether we are baking a cake, building a house, or studying science. But what exactly is measurement, and how do we make sense of the different types, scales, and units? This article will take you through the world of measurement and explain these concepts in detail.
Definition of Measurement
Measurement is the process of determining the size, length, amount, or degree of something using specific tools or instruments. It allows us to quantify and compare different attributes of objects or phenomena, making it possible to communicate information accurately and objectively.
Types of Measurement
There are various types of measurement, each serving a different purpose. Here are some common types:

- Length: It refers to the distance from one end of an object to the other. It is commonly measured in units such as metres (m), centimetres (cm), and inches (in).
- Mass: Mass is the measurement of the amount of matter in an object. Common units for mass include grams (g), kilograms (kg), and pounds (lb).
- Volume: Volume measures the amount of space an object occupies. It is often measured in litres (L), millilitres (mL), and cubic metres (m³).
- Temperature: Temperature measures an object or environment’s degree of heat or coldness. It is measured in degrees Celsius (°C), degrees Fahrenheit (°F), and Kelvin (K).
- Time: Time is the measurement of the duration of events or the intervals between them. Units of time include seconds (s), minutes (min), and hours (h).
- Area: Area measures the surface of an object. Common units include square metres (m²), square centimetres (cm²), and square feet (ft²).
- Speed: Speed is the measure of how fast an object is moving. It is typically measured in metres per second (m/s), kilometres per hour (km/h), and miles per hour (mph).
Measurement Scales
Measurement scales refer to the different ways that variables can be measured. There are four main types of measurement scales:
- Nominal Scale: The nominal scale is the simplest form of measurement and is used to label variables without any quantitative value, such as gender (male/female) or hair colour (blonde, brunette, redhead).
- Ordinal Scale: The ordinal scale provides a rank order to the variables but does not specify the exact differences between them. For example, finishing positions in a race (1st, 2nd, 3rd) or levels of satisfaction (such as satisfied, neutral, dissatisfied).
- Interval Scale: The interval scale provides order and the exact differences between the values. However, it does not have a true zero point. For example, the temperature is Celsius or Fahrenheit.
- Ratio Scale: The ratio scale is the most informative, providing order, exact differences, and a true zero point. Examples include weight, height, and age.
Units of Measurement
Units of measurement provide standard quantities used to express and compare measurements. Here are some common units for different types of measurements:
Length –
- Millimetre (mm): A small unit of length used for precise measurements.
- Centimetre (cm): Commonly used for measuring shorter lengths.
- Metre (m): The base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI).
- Kilometre (km): Used for measuring longer distances.
Mass –
- Milligram (mg): A very small unit of mass.
- Gram (g): The base unit of mass in the SI system.
- Kilogram (kg): Commonly used for measuring larger masses.
Volume –
- Millilitre (ml): A small unit of volume.
- Litre (l): The base unit of volume.
- Cubic metre (m³): Used for measuring large volumes.
Temperature –
- Degrees Celsius (°C): Commonly used in most countries for everyday temperature measurements.
- Degrees Fahrenheit (°F): Used primarily in the United States.
- Kelvin (K): The base unit of temperature in the SI system, used in scientific contexts.
Time –
- Second (s): The base unit of time in the SI system.
- Minute (min): Equal to 60 seconds.
- Hour (h): Equal to 60 minutes.
Metric vs. Imperial Systems
- Metric System: This is used by most countries around the world. It is based on units of 10, which makes it easy to convert between units (e.g., 1 metre = 100 centimetres).
- Imperial System: Used mainly in the United States, it includes units like inches, feet, pounds, and gallons. Conversions can be more complex (e.g., 1 foot = 12 inches).
Interesting Measurement Tools
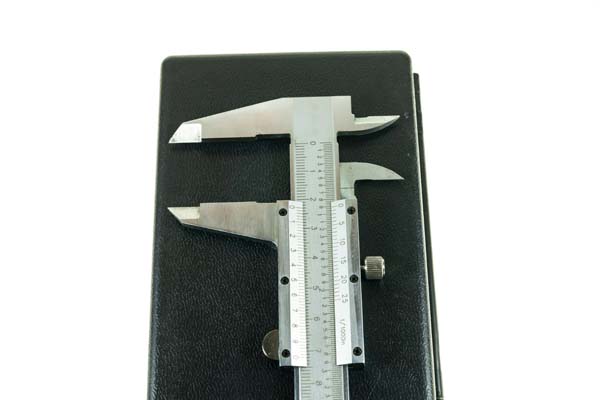
- Callipers: Used to measure the distance between two opposite sides of an object. They can be very precise, down to fractions of a millimetre.
- Seismograph: Measures the intensity of earthquakes by detecting and recording seismic waves.
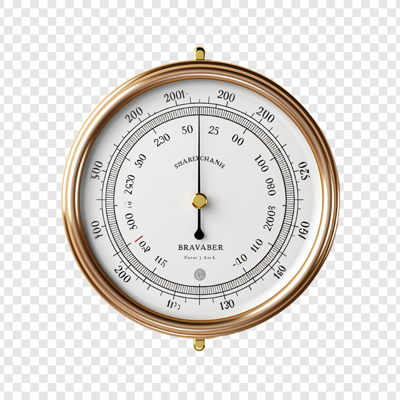
- Barometer: Measures atmospheric pressure, which helps forecast weather.


Conversion Facts
Temperature Conversions:
To convert Celsius to Fahrenheit:
F = ( C × 9 / 5 ) + 32
To convert Fahrenheit to Celsius:
C = ( F − 32 ) × 5 / 9
Interesting Facts about Measurement
- Historical Units: Ancient Egyptians used their system of measurement called “cubits” to construct the pyramids. A cubit was the length from the elbow to the tip of the middle finger.
- Atomic Clocks: The most accurate timekeepers in the world are atomic clocks, which can measure time to within a few billionths of a second!
- Temperature Extremes: The hottest temperature ever recorded on Earth was 56.7°C (134°F) in Death Valley, California, while the coldest was -89.2°C (-128.6°F) in Antarctica.
Conclusion
Understanding measurement is fundamental to science, engineering, and everyday life. It allows us to quantify and make sense of the world around us. By knowing the different types, scales, and units of measurement, we can communicate information accurately and make informed decisions.
For more such informative/interesting blogs, visit Center Point School.